N3C Privacy-Preserving Record Linkage
Enabling Data connectivity | Ensuring Data Security
Privacy-preserving record linkage (PPRL) marks a major next step for N3C. It significantly expands this already groundbreaking scope of secure patient-level data and unlocks exciting new opportunities for clinicians, researchers, and patients to better understand diseases. How does it accomplish this? Read more below to find out.
N3C PPRL Introduction
3 Key Definitions
Privacy-Preserving Record Linkage (PPRL): A means of connecting records using secure, pseudonymization processes in a data set that refer to the same individual across different data sources while maintaining the individuals’ privacy.
Linkage Honest Broker Agreement (LHBA): A three-way agreement that is intended for execution between an N3C data participant, NCATS, and Regenstrief in its role as the linkage honest broker. A linkage honest broker in the PPRL’s infrastructure is a party that holds de-identified tokens (“hashes”) and operates a service that matches tokens generated across disparate datasets to formulate a single Match ID for a specific use case.
De-identified Tokens: To facilitate the PPRL process, N3C data participants use software to generate de-identified tokens. These tokens prevent the identity of patients from being revealed during any stage of the PPRL process. N3C data participants send de-identified tokens to the designated N3C Linkage Honest Broker. The N3C de-identified tokens are held separately from data residing within the N3C data enclave.
3 Steps for Institutions to join PPRL
- Agree and sign the Datavant software license agreement
- Agree and sign the Linkage Honest Broker Agreement (LHBA)
- Apply the de-identified tokens and Pseudo ID to the data already being sent to N3C
N3C PPRL Principles
N3C Participating Sites to the N3C Data Enclave
- Participation in the PPRL is voluntary.
- Per existing procedures, Participating Sites must also have a signed Data Transfer Agreement (DTA) to transfer their electronic health record data (EHR) (in the form of a Limited Data Set) to the N3C Data Enclave.
- Only the participating sites have access to and control of Personal Health Information and Personally Identifying Information (PHI/PII) (actual identifiers).
- Participation is not an all or none proposition for all linkage activities. Participation in PPRL obligates participating institutions to de-duplication of duplicate records and is necessary for accuracy of counts and prevalence information. Linkage of multiple datasets and cohort discovery are optional activities.
- Participation is controlled (see below) and pre-determined by the participating sites.
- Participating sites may discontinue participation in the Linkage Honest Broker Agreement at any time (see below). However, if an investigator is actively using data for linkage at the time of discontinuance, that investigator will be allowed complete their work.
Linkage Honest Broker (LHB)
- The Linkage Honest Broker for N3C is the Regenstrief Institute. The LHB is a neutral entity located outside of the N3C Data Enclave that serves as an escrow for the cryptographic hash codes (tokens), operates the technology platform which facilitates PPRL using these tokens.
- The LHB does NOT receive, store, or process PHI/PII or clinical information. As aforementioned the PHI/PII is ONLY held by the data participating sites. For the avoidance of doubt, Regenstrief may utilize tokens and metadata at the request of a Participating Site and consistent with the NCATS N3C Data Enclave rules and policies for possible follow-on clinical research.
- The LHB will hold certain metadata such as the originating data contributor/data source, and the nature of data associated with the received tokens, e.g., EHR data, chest x-ray, viral variant data. The LHB is contracted by NCATS.
Exclusions of Use
- Linked datasets will be used for scientific research only. Uses for administrative and performance measurements/assessments are not permitted.
- Data participating sites within N3C are providing clinical data to advance research. Data cannot be used for administrative or performance metrics such as quality, reimbursement, and medical errors.
Ways to Participate
Key concept: De-identification
Making sure that personally identifiable information (PII) in patient records never leaves contributing sites is a core aspect of N3C PPRL and the three ways of participating in it:
**- De-duplication
- Multi-Dataset Linkage
- Cohort Discovery**
Read more below to learn how de-identification is incorporated in each of the PPRL participation options.
De-duplication

“De-duplication” means eliminating duplicate or redundant information within a data source and among two or more datasets. In the context of N3C, linkage with de-duplication means combining the data from medical records of a unique patient that for some reason has repeated records (duplicates). Multiple records for a unique patient is surprisingly common and can happen for a variety of reasons such as being registered under different names (maiden and married surname), multiple registrations caused by misspellings, or the combining of multiple institutions records where the same patient may have gotten care. De-duplication takes place within the N3C Data Enclave (see Image: Illustrates de-duplication process frommultiple institutions), identifies data records associated with unique individuals with multiple records and allows an N3C Data user (investigator) to adjust for counts in their analysis.
De-duplication is a requirement for any institution that participates in the LHBA, because of its importance to the data quality of the N3C Data Enclave and its scientific mission.
De-duplication requires a data contributing site to:
- Apply the cryptographic hash code (token) to relevant patient records.
- Send the cryptographic hash code (token) with metadata to the linkage honest broker.
- Include the cryptographic hash code (token) as part of the N3C data transfer payload.
- Allow N3C to use the cryptographic hash code (token) to de-duplicate redundant information.
Linking Multiple Datasets

Though there are many types of datasets and ways to link to them, the Linkage Honest Broker Agreement applies only to datasets that are within the N3C Data Enclave and requires linkage using the hash/PPRL. N3C has developed an external dataset classification system that the LHBA only applies to datasets classified as class “0” and Class “2”. Linkages to external datasets that do not require the hash or PPRL are not covered by this agreement. The difference between Class 0 datasets and Class 2 datasets is Class 0 datasets originate from different enclaves and allows for a temporary extension of the N3C Data Enclave to accommodate this requirement. If additional computational resources are required for large datasets, the N3C Data Enclave will utilize NCATS High PC Performance Computing (HPC) services for data processing.
Multi-Dataset Linkage Classification Summary:
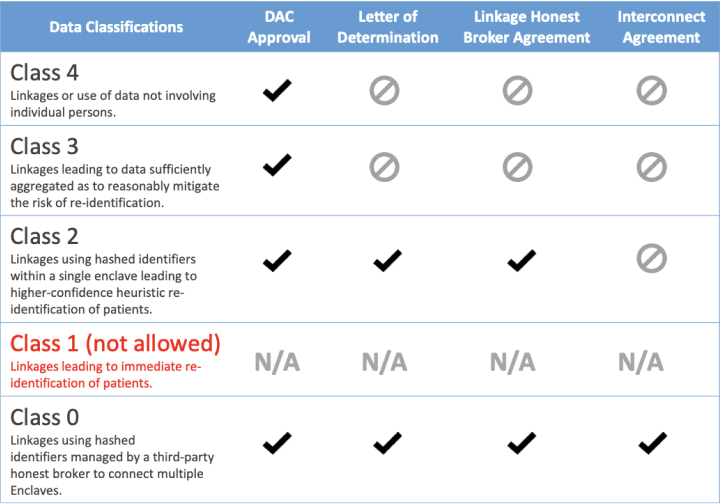
Access to various classes of data require sets of agreements to be in place for the data requesters. All datasets that use the PPRL (Class 0 and 2) are considered level 3 data and as such must work through their institutional policies and require a letter of determination when submitting an N3C Data Use Request (DUR). Additional information on terms of use for available linkable datasets can be found at the discover.biothings Dataset Registry.
Class 2 dataset linkages require existing institutional N3C Data Use Agreement, Dual authentication and authorization, a signed institutional linkage honest broker agreement for multiple datasets, an approved data use request (DUR) by the federally staffed data access committee (DAC), and local institutions IRB letter of determination. IRBs must clearly have reviewed the DURs proposed protocol and the specific use of multiple datasets beyond N3C EHR-derived data. Class 2 dataset linkage are contained within the single N3C Data Enclave. An example of a class 2 multiple linkage datasets would be if N3C data is linked to Mortality data that was sent to N3C.
For class 0 dataset linkages, that connect more than one enclave, an additional interconnect agreement will be in place. The interconnect agreement will be agreement between two trusted enclaves in order to instantiate what is referred to as a temporary virtual or ephemeral workbench. The workbench is ephemeral because it is short-lived for a specific task and then destroyed when an investigator's work is completed.
Classes 3 and 4 require a DUR for the study approved by the DAC.
Cohort Discovery
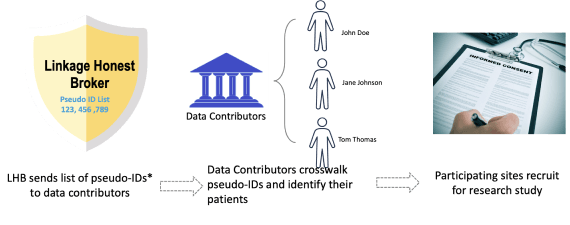
The third and final type of linkage is cohort discovery. Cohort Discovery is a web-based tool that allows researchers to discover research-specific population cohorts across multiple linked datasets within N3C. Cohort discovery is a common and familiar process to many data participating sites that participate in networks like TriNetX or Accrual to Clinical Trials (ACT) activity. In the ideal world, prior to asking sites to do cohort discovery for a clinical study, an organization has done feasibility research that confirms there is a large enough population exists to power a study. Once all of feasibility research is determined only then are sites contacted with potential list of de-identified patient keys sent to a data contributor for cohort discovery by the LHB. Interested sites can decide to participate or not in any particular study. Only the participating sites are technically able to re-identify patients. If a site chooses to participate in any given study, the recruitment process follows local institutional policy and procedures on contacting patients and consenting them for a study (see Image: Cohort Discovery Prospective Study Process). Cohort discovery is key to use-cases that require recruitment of patients from a de-identified (but PPRL-ready) cohort or when certain prospective data or local data augmentations is required. Those use-cases should follow both N3C and local institutional governance and be reviewed and approved by both IRBs of record.
It is very important that cohort discovery not be conflated with patient re-identification. In cohort discovery ONLY participating sites that have signed the LHBA and opted for cohort discovery can re-identify their own patients. The linkage honest broker list of de-identified patient keys does not have any Personally Identifying Information, (PII).
The requirements for cohort discovery are as follows:
- Tokens from N3C participating sites will be linkable to other linkable datasets for the purpose of study feasibility assessments.
- Research feasibility requests may be initiated by authorized researchers, and NIH for its operational purposes.
- Compliance with the N3C download policy or cell sizes < 20 and data release policies for aggregate counts, which are considered will apply.
- The Linkage Honest Broker results will only include aggregate counts and will not include row level data or participating site information.
Governance & Oversight
There are several considerations related to the technical and data governance architecture for the N3C PPRL linked data infrastructure:
- Tokens only reside with the Linkage Honest Broker
- Data resides and is unified in the authorized data enclaves: 1) N3C data and linkable datasets that will be available within the N3C environment will be available for authorized researchers within the N3C analysis workspace, 2) the ephemeral (Virtual Machine, (VM)) workbench connecting multiple enclaves is an extension of the N3C Data Enclave, where datasets will be unified based on data governance approvals.
- The Linkage Honest Broker platform produces (or will produce) a linkage dashboard depicting the linkages in records between disparate datasets.
- An authentication and authorization system managed by the NIH will determine the nature of information that can be shared with the requesting party.
Multiple Enclave Process:
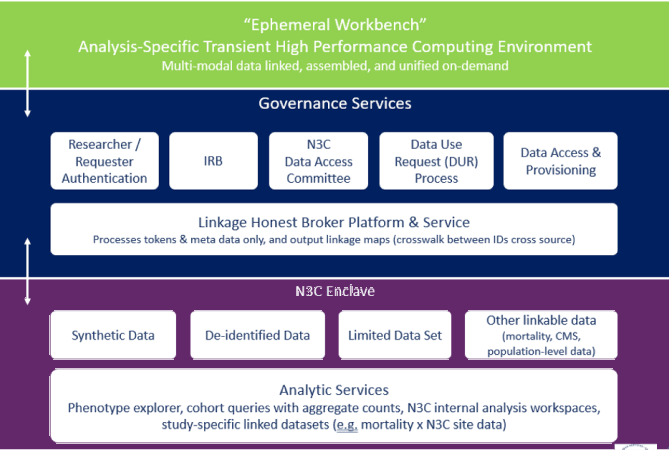
Note: De-identified data refers to level 2 requested access, where 17 of 18 HIPAA identifiers have been removed; longitudinal data are data-shifted to protect individual privacy. The Limited Data Set (LDS) available from N3C consists of health information from individuals. Data will also be collected from individuals infected with pathogens such as SARS 1, MERS, and H1N1 to support comparative studies. 16 of 18 HIPAA identifiers have been removed; data retain dates and zip codes.
Linkage Honest Broker Platform and Service
The Linkage Honest Broker platform and service will interface with the relevant Researcher/Requester Authentication Systems, the N3C Data Enclave, and the ephemeral workbench environments.
- NIH staff and registered N3C Data Enclave investigators will have access to the Linkage Honest Broker platform for an aggregate-level view of overlaps between disparate datasets and repositories.
- The Linkage Honest Broker platform will hold all tokens centrally in its role as a privacy escrow for de-identified, linkable tokens.
- The platform will ingest and run linkages on all tokens held centrally and sent to it by various participating sites and repositories. The platform will generate linkage maps that can only be accessed by other platforms based on data governance authorizations. See illustration below for the interfaces between the Linkage Honest Broker platform and the N3C Data Enclave.
Interfaces between the Linkage Honest Broker platform and the N3C Data Enclave:
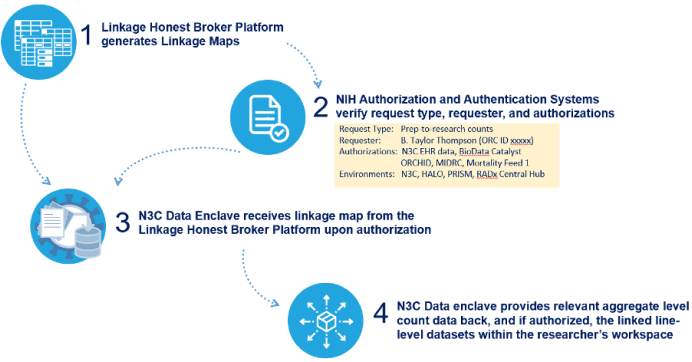
Example PPRL Use Case with Mortality Data
Requirements for Actors Involved in Governance & Oversight
Data Contributors / NCATS / Regenstrief Sign Linkage Honest Broker Agreement
- Allows data transfer of EHR data into the N3C enclave
- Site agreement to apply the Hash/PPRL
- Allows the linkage between an external mortality dataset and their EHR Data
- Applies N3C/NCATS Governance and Policy to process (N3C community and NCATS as steward of the data)
Data Contributors / Datavant Implement PPRL Software
- Sign License agreement with Datavant (no cost)
- Install Datavant software
- Apply PPRL using Datavant tool
Data Contributors Payload Transfer
- Send PPRL tokens (No PHI/PII or Clinical information) to Regenstrief Institute, the linkage honest broker
- Send data payload to N3C
NCATS Modify NIH IRB
- N3C IRB protocol amendment to add mortality data Mortality Harmonization
- Harmonization, quality assurance, quality control Modify DAC
- Add Mortality to DAC process
FAQs
This section answers a variety of questions regarding the general purpose and use of any PPRL datasets residing in the N3C Enclave. For a list of FAQs that are specific to each PPRL dataset, please go to the FAQ for N3C PPRL Datasets page.
Privacy-preserving record linkage (PPRL) is a means of connecting records using secure, pseudonymization processes in a data set that refer to the same individual across different data sources while maintaining the individuals’ privacy. Supported by a contract from the NIH, Regenstrief will serve as the national project’s linkage honest broker, using specialized technologies and processes to create more complete and informative data sets.
Supported by a contract from NCATS, the Regenstrief Institute will serve as the N3C’s Linkage Honest Broker, using Datavant software, and processes to allow the N3C enclave the ability to create more complete and informative data sets.
The LHB handles requests for data linkages from authorized users and manages the privacy preserving record linkage (PPRL) process, which uses technologies and approaches that help ensure N3C data are shared safely, securely, and privately, all in compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) standards. Linking de-identified N3C data through requests to the LHB will help to address the challenges of securely assembling patient-level data that is traditionally fragmented and difficult to use across large-scale clinical research efforts. The LHB never receives or has access to the Personal Health Information (PHI) and Personally Identifiable Information (PII) that is held by the participating sites.
The LHBA is a 3-way agreement that is intended for execution between an N3C data contributing organization (the participating site), NCATS, and the Regenstrief Institute in its role as the Linkage Honest Broker (LHB). The LHB in NCATS’ privacy preserving record linkage infrastructure is the party that holds de-identified patient keys (also called “hashes”). The patient keys allow the matching of individual without containing PII/PHI, and Regenstrief Institute operates a service that matches patient keys generated across different datasets to formulate a match or linkage.
Signing the LHBA obligates a PPRL participating site to de-duplication of redundant information. The other functions – linkage to other data sets (such as Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services data, mortality data and viral variant data) and participation in cohort discovery – are optional.
Yes, at any time, each site can change its participation in the PPRL. However, if an investigator is actively using data for linkage at the time of discontinuance, that investigator will be allowed complete their work.
Send all questions about the LHB or the LHBA to NCATS’ Office of Strategic Alliances at NCATSPartnerships@mail.nih.gov (link sends e-mail).
Only Authorized Organizational Officials that contribute data to the N3C Data Enclave can sign the LHBA.
Submit an N3C Service Desk ticket here. Choose the option "N3C Record Linkage" and PPRL Question Category "Regenstrief Institute."
No, you do not need to reinstall Datavant software if you are using Datavant for your other projects. For your N3C implementation, Datavant will provide you with the N3C-specific configurations that support the generation of N3C de-identified tokens, and assign data governance rights for your site to generate tokens that can be processed only by the N3C linkage honest broker.
Submit an N3C Service Desk ticket here. Choose the option "N3C Record Linkage" and PPRL Question Category "Datavant Software Questions."
Several resources are available within the Enclave to learn more about PPRL. Users can access the PPRL Introduction Module, as well as the Introduction to Privacy-Preserving Record Linkage (PPRL) for N3C Researchers training course, to learn more about PPRL, how to access it, how to use it, as well as other helpful tips.
Glossary of Terms
Authentication: The act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user.
Authorization: The function of specifying access rights/privileges to resources.
Cohort Discovery: The process for enabling authorized researchers to query the N3C Data Enclave for data records associated with de-identified individuals and meet specified inclusion and exclusion criteria.
De-duplication: Eliminating duplicate or redundant information within a data source.
De-identified Patient Keys: Encrypted strings that are processed through a cryptographic method called “hashing,” with the resulting output referred to hashes; these are referred to as tokens more generally. Datavant de-identified patient keys are certified as de-identified per the HIPAA Privacy Rule. Note: Not all hashes and hashing are considered de-identified per HIPAA.
De-identification: The process of removing identifiers from Protected Health Information per HIPAA. There are two acceptable methods to render data de-identified in a HIPAA-compliant manner: 1) Safe Harbor – removal of the 18 identifiers, or 2) Expert Determination Method, which requires a statistical assessment of de-identification. With standard Safe Harbor de-identification, too much data fidelity is lost, such as with dates of service. Current N3C data meets the standard of limited data. When Privacy-Preserving Record Linkage methods are applied within N3C, the data linkages occur in a de-identified manner through the use of de-identified tokens. The linked datasets may then meet the relevant data standards and data uses in accordance with N3C policy.
Health Data: The Participating Site’s information related to an individual’s medical history, including but not limited to structured information such as demographics, vital signs, diagnoses, procedures, admission, discharge and transfer information and semi-structured information, including laboratory tests and results, medications, imaging, waveform, variants etc. Health Data that includes real dates and zip codes is a Limited Data Set as defined herein. Health Data is referenced in the Data Transfer Agreement as Data.
Investigator Data Access: Investigators that meet requirement to use different types of data must include but not limited to a data use request, letter of determination, Data Access Committee approve and interconnect agreement.
Interconnect Agreement (ICA): Sharing agreements between enclaves, such as Enclave entities like NIBIB Medical Imaging and Data Resource Center (MIDRC), and NCATS N3C.
Linked ID: When the linkage honest broker generates a link between two cryptographic hash codes (tokens), they also generate a new random ID that corresponds to the linkage itself; this is the Linked ID. Using unique Linked IDs ensures that the linkages can be used only where data governance restrictions allow.
Limited Data Set: The Limited Data Set (LDS) available from N3C consists of health information from individuals who have received a COVID-19 test or whose symptoms are consistent with COVID-19. Data will also be collected from individuals infected with pathogens such as SARS 1, MERS, and H1N1 to support comparative studies. 16 of 18 HIPAA identifiers have been removed; Data retain dates and zip codes. of service and zip codes. "Metadata" means a set of data that provides a structural or administrative description about the Participating Site’s Health Data. Metadata does not include Health Data.
Metadata: A set of data that provides a structural or administrative description about the Participating Site’s Health Data. Metadata does not include Health Data.
Privacy-Preserving Record Linkage (PPRL): 1) Connecting records using secure, pseudonymization processes in a data set that refer to the same individual across different data sources while maintaining the individuals’ privacy. 2) A Method to generate de-identified patient keys (“hashes”) that enable data likability.
Pseudo ID: Originating from an institution or source system, these are randomly generated IDs that accompany the de-identified patient keys / hashes when sent to the third-party linkage honest broker.
Research: A systematic investigation, including research development, testing, and evaluation designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.
Site Permission for Linkage: Determines whether a site’s data can be included in linkage studies.
Token, or Hash: An encrypted value created by an irreversible conversion algorithm and any underlying Protected Health Information that has been de-identified using the expert determination method as described under HIPAA regulations at 45 CFR 164.515(b)(1).
